欢迎转载,转载请注明出处 xianzhu21.space。
RIL 简介
RIL(Radio Interface Layer) 是一种 HAL(Hardware Abstraction Layer),它提供控制 Modem 的统一接口。而 RILJ 是一种给 Java 层提供与 RIL 通信的Android Framework 层服务。RILJ 通过 Unix Socket 与 RIL 守护进程通信,可以说 RILJ 是Telephony 框架中 Java 层的最底层。
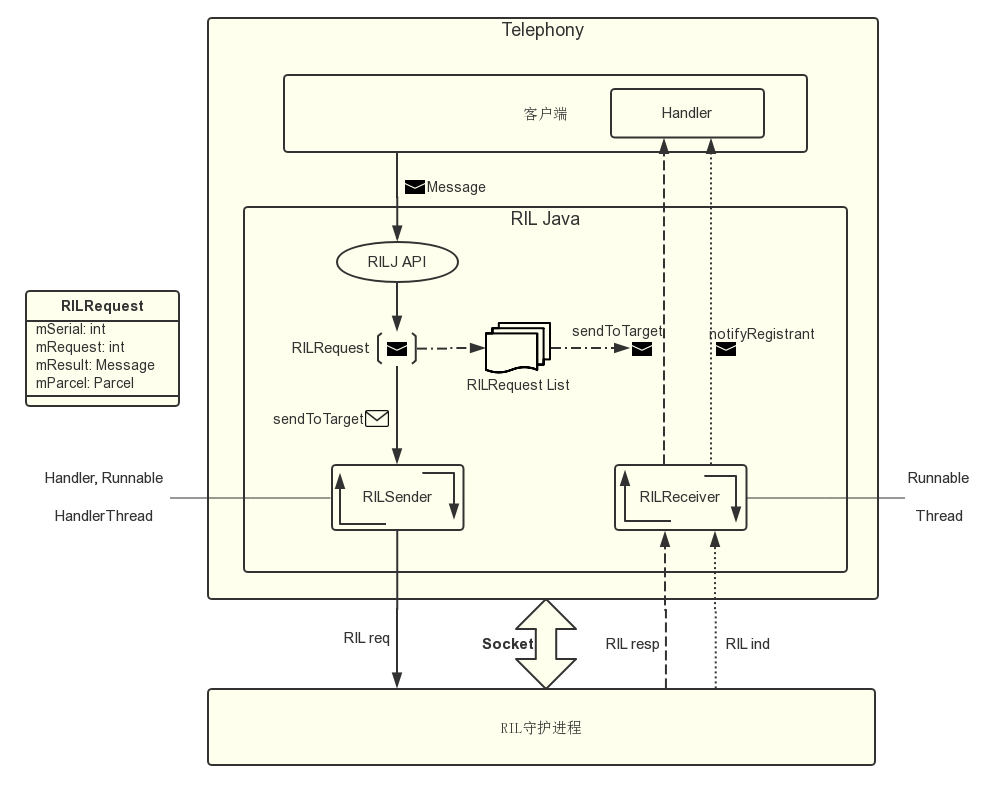
RILJ 有 2 种服务机制——req/resp 和 ind 服务。因为网络服务需要异步操作,RILJ 中有 2 个线程——RILSender 和 RILReceiver,分别处理向 RIL 守护程序发送数据和从 RIL 守护程序接收数据。
req/resp 服务机制
req/resp服务机制的流程是
- 客户端发送特定类型的 Message 对象给 RILJ
- RILJ 用 Message 对象生成 RILRequest 对象,发送给 RILSender 线程
- RILSender 线程先把 RILRequest 对象加到 RILRequest List,然后将 RILRequest 对象的数据序列化后用 Socket 发送给 RIL 守护进程
- RILReceiver 接收 RIL 守护进程发送的结果,并从 RILRequest List 中找到相应的 RILRequest,取出客户端发送的 Message 对象,把结果存到 Message 对象中并发送给客户端的 Handler 对象
- 客户端的 Handler 对象根据 Message 对象类型处理结果
下面结合源码一一分析每一个步骤。以 Android 6 源码分析,但 Android 4, 5, 6 的 MO 在 RIL 部分的代码基本没有改变。
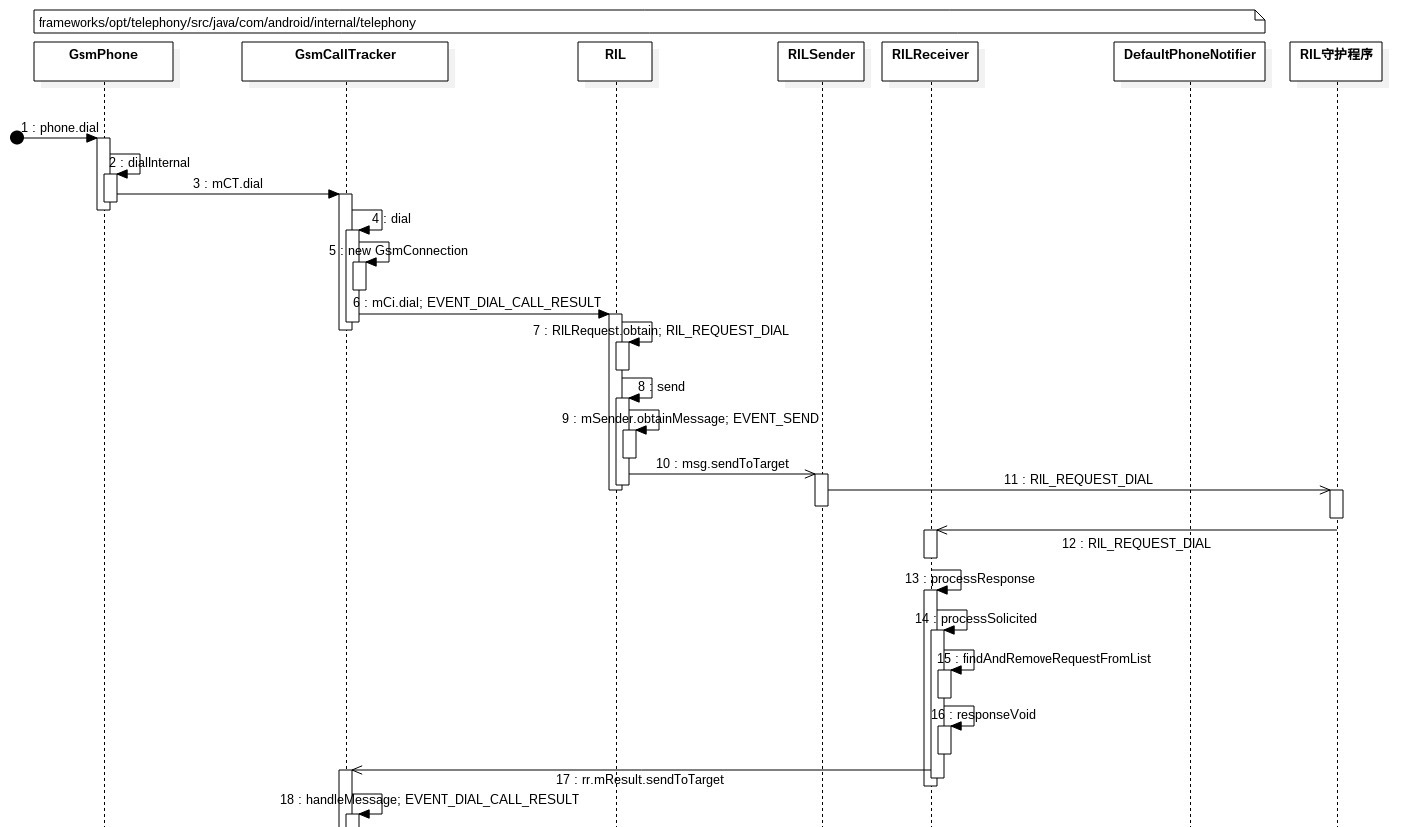
上图是 MO (Mobile Origination, 即拨打电话) 在 Framework 层的时序图。
1. 客户端发送给 RILJ
首先 Phone(GsmPhone 为例,CdmaPhone 类似)对象调用 GsmCallTracker(继承自 Handler)对象的 dial,GsmCallTracker 对象调用 CommandInterface对象 (即RIL对象)的dial方法。
/* GsmCallTacker.java */
synchronized Connection dial (String dialString, int clirMode, UUSInfo uusInfo, Bundle intentExtras)
throws CallStateException {
...
// 调用CommandInterface对象,即RIL对象的dial()方法
// obtainCompleteMessage(EVENT_DIAL_CALL_RESULT)方法是获取
// msg.what为EVENT_DIAL_CALL_RESULT的Message对象
mCi.dial(mPendingMO.getAddress(), clirMode, uusInfo,
obtainCompleteMessage(EVENT_DIAL_CALL_RESULT));
...
}
2. RILJ 发送给 RILSender 线程
接下来分析RIL的dial方法。
/* RIL.java */
@Override
public void dial(String address, int clirMode, UUSInfo uusInfo, Message result) {
// 获取RILRequest对象,包含客户端传递的Message对象
RILRequest rr = RILRequest.obtain(RIL_REQUEST_DIAL, result);
// 写入数据
rr.mParcel.writeString(address);
rr.mParcel.writeInt(clirMode);
...
send(rr);
}
RIL 的 dial 方法中利用 GsmCallTracker 传递过来的 Message 对象获取 RILRequest 对象。RILRequest 类主要有 4 个成员变量。int mSerial 是用来唯一标识 RILRequest 对象的变量,int mRequest 是 RILSender 用于区分 RILRequest 类型的变量,MO 中为 RIL_REQUEST_DIAL,Message mResult 是存储结果的 Message 对象,是从 GsmCallTracker 传递过来的,Parcel mParcel 是存储请求数据的 Parcel 对象。
/* RIL.java */
static RILRequest obtain(int request, Message result) {
RILRequest rr = null;
synchronized(sPoolSync) {
if (sPool != null) {
rr = sPool;
sPool = rr.mNext;
rr.mNext = null;
sPoolSize--;
}
}
if (rr == null) {
rr = new RILRequest();
}
// 唯一序列号
rr.mSerial = sNextSerial.getAndIncrement();
// RILRequest类型
rr.mRequest = request;
// 用来保存结果的Message对象,从客户端传递过来
rr.mResult = result;
// 获取用来存储请求数据的Parcel对象
rr.mParcel = Parcel.obtain();
if (result != null && result.getTarget() == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("Message target must not be null");
}
// first elements in any RIL Parcel
rr.mParcel.writeInt(request);
rr.mParcel.writeInt(rr.mSerial);
return rr;
}
接下来调用 RIL 的 send 方法,传递刚获取到的 RILRequest 对象。send 方法将 RILRequest 对象存到 Message 对象后发送给 RILSender 处理。
/* RIL.java */
private void send(RILRequest rr) {
Message msg;
if (mSocket == null) {
rr.onError(RADIO_NOT_AVAILABLE, null);
rr.release();
return;
}
// 获取RILSender的Message对象
msg = mSender.obtainMessage(EVENT_SEND, rr);
acquireWakeLock();
// Message对象发送给RILSender对象
msg.sendToTarget();
}
3. RILSender 线程发送给 RIL 守护进程
接下来我们来分析 RILSender 的工作机制。
RILSender 继承自 Handler,实现了 Runnable 接口。RIL 在构造方法中创建 HandlerThread 线程来执行 RILSender。
/* RIL.java */
public RIL(Context context, int preferredNetworkType, int cdmaSubscription, Integer instanceId) {
...
mSenderThread = new HanlderThread("RILSender" + mInstanceId);
mSenderThread.start();
Looper looper = mSenderThread.getLooper();
mSender = new RILSender(looper);
...
}
RILSender 接收 RIL 发送的 Message 对象后在 handleMessage 方法中处理 RILRequest 对象,然后利用 RILReceiver 创建的 LocalSocket 对象把 RIL req 数据发送给 RIL 守护进程。
/* RIL.java */
class RILSender extends Handler implements Runnable {
public RILSender(Looper looper) {
super(looper);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// 从Message对象取RILRequest对象
RILRequest rr = (RILRequest)(msg.obj);
...
switch (msg.what) {
case EVENT_SEND:
try {
LocalSocket s;
// mSocket为RILReceiver创建的LocalSocket对象
s = mSocket;
...
byte[] data;
// 对Parcel对象编组,以便用Socket发送给RILC
data = rr.mParcel.marshall();
// 把RILRequest对象加入到RILRequest List,以便RIL resp服务查找
synchronized (mRequestList) {
mRequestList.append(rr.mSerial, rr);
rr.mParcel.recycle();
rr.mParcel = null;
}
...
// parcel length in big endan
dataLength[0] = dataLength[1] = 0;
dataLength[2] = (byte)((data.length >> 8) & 0xff);
dataLength[3] = (byte)((data.length) & 0xff);
// 发送给RIL守护进程
s.getOutputStream().write(dataLength);
s.getOutputStream().write(data);
} catch ...
break;
...
}
}
}
4. RILReceiver 接收 RIL 守护进程发送的结果,处理后发送给客户端的 Handler
首先从 socket 中读取数据,然后根据类型(resp 服务或 ind 服务)处理。从 mRequestList 中根据 serial 值取出 RILRequest 对象并删除。然后从RILRequest 对象中取出客户端的 Message 对象,把 rild 返回的数据存到 Message 对象中,然后发送给客户端来处理返回的数据。
/* RIL.java */
class RILReceiver implements Runnable {
byte[] buffer;
...
@Override
public void
run() {
...
try {
// 连接rild的socket
s = new LocalSocket();
l = new LocalSocketAddress(rilSocket,
LocalSocketAddress.Namespace.RESERVED);
s.connect(l);
} catch (IOException ex){
...
}
// 把socket保存到mSocket成员变了,共RILSender调用
mSocket = s;
...
int length = 0;
try {
InputStream is = mSocket.getInputStream();
for (;;) {
Parcel p;
// 从socket中读取数据存到buffer
length = readRilMessage(is, buffer);
if (length < 0) {
// End-of-stream reached
break;
}
// 把数据反编组保存到Parcel对象中
p = Parcel.obtain();
p.unmarshall(buffer, 0, length);
p.setDataPosition(0);
// Rlog.v(RILJ_LOG_TAG, "Read packet: " + length + " bytes");
// 处理数据
processResponse(p);
p.recycle();
}
} catch {}
...
}
}
private void processResponse (Parcel p) {
int type;
type = p.readInt();
if (type == RESPONSE_UNSOLICITED) {
// 处理ind服务,即rild自发发送的数据
processUnsolicited (p);
} else if (type == RESPONSE_SOLICITED) {
// 处理resp服务,即请求rild后返回的数据
RILRequest rr = processSolicited (p);
if (rr != null) {
rr.release();
decrementWakeLock();
}
}
}
private RILRequest processSolicited (Parcel p) {
int serial, error;
boolean found = false;
serial = p.readInt();
error = p.readInt();
RILRequest rr;
// 在mRequestList中取出RILRequest对象,然后删除
rr = findAndRemoveRequestFromList(serial);
...
if (error == 0 || p.dataAvail() > 0) {
try {switch (rr.mRequest) {
...
// responseVoid方法中直接返回null
case RIL_REQUEST_DIAL: ret = responseVoid(p); break;
...
}} // catch {}
}
...
if (error == 0) {
if (rr.mResult != null) {
// 处理RILRequest对象的数据
// 用AsyncResult对象包一下m.obj和ret然后再赋给m.obj
/*
public static AsyncResult
forMessage(Message m, Object r, Throwable ex) {
AsyncResult ret;
ret = new AsyncResult (m.obj, r, ex);
m.obj = ret;
return ret;}
*/
AsyncResult.forMessage(rr.mResult, ret, null);
// 发送给客户端的Handler对象来处理
rr.mResult.sendToTarget();
}
}
return rr;
}
5. 客户端的 Handler 对象根据 Message 对象类型处理结果
GsmCallTracker 对象处理返回的 Message 对象
/* GsmCallTracker.java */
@Override
public void handleMessage (Message msg) {
AsyncResult ar;
...
switch (msg.what) {
...
case EVENT_DIAL_CALL_RESULT:
ar = (AsyncResult) msg.obj;
if (ar.exception != null) {
log("dial call failed!!");
mHelper.PendingHangupRequestUpdate();
}
operationComplete();
break;
...
}
}
RILJ 的 req/resp 服务的整个流程如下图所示。
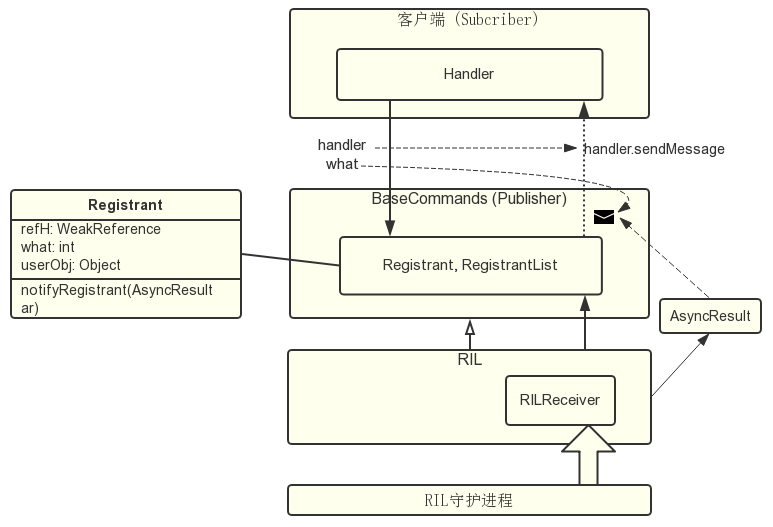
ind 服务机制
ind 服务机制的流程是
- RILReceiver 从 rild 获得消息,然后在 processUnsolicited 方法中根据 reponse 类型获得底层传过来的数据。
- 再根据 response 类型,调用相应的 Registrant 对象的 notifyRegistrant 方法或 RegistrantList 对象的 notifyRegistrants 方法。
- 把数据封装成 AsyncResult 对象,发送给相应的注册对象。
我们以来电为例来说明 ind 服务的流程。
1. RILReceiver 获取 rild 发来的消息
第一步跟 req/resp 服务中 RILReceiver 接收消息的代码一致,在 processResponse 方法中 ind 服务的消息会调用 processUnsolicited 方法。这里不再赘述。
2. 调用相应的 Registrant 对象的 notifyRegistrant 方法
下面的代码是 processUnsolicited 方法的处理过程,最后会调用 mRingRegistrant 的 notifyRegistrant 方法。
/* RIL.java */
private void processUnsolicited (Parcel p) {
int response;
Object ret;
response = p.readInt();
try {switch(response) {
...
// 从 Pacel 对象中获取数据,保存在 char 数组中
case RIL_UNSOL_CALL_RING: ret = responseCallRing(p); break;
}} // catch
switch(response) {
...
case RIL_UNSOL_CALL_RING:
if (RILJ_LOGD) unsljLogRet(response, ret);
if (mRingRegistrant != null) {
// mRingRegistrant不空说明有注册对象,调用notifyRegistrant方法来通知注册对象
mRingRegistrant.notifyRegistrant(new AsyncResult (null, ret, null));
}
break;
...
}
}
mRingRegistrant 是 Registrant 对象,Registrant 机制其实是订阅者模式。RIL 继承自 BaseCommand 类,Registrant 对象和 RegistrantList 对象是在BaseCommand 中创建的,因此 RIL 类也拥有 mRingRegistrant。
3. 把数据发送给相应的注册对象
在这里首先说明 Registrant 的机制,先看下 Registrant 类的代码。
/* Registrant.java */
public class Registrant
{
public Registrant(Handler h, int what, Object obj)
{
refH = new WeakReference(h);
this.what = what;
userObj = obj;
}
// 这个方法还有其他3个方法重载,参数分别是空、Object对象和Throwable对象
public void notifyRegistrant(AsyncResult ar)
{
internalNotifyRegistrant (ar.result, ar.exception);
}
/*package*/ void internalNotifyRegistrant (Object result, Throwable exception)
{
Handler h = getHandler();
if (h == null) {
clear();
} else {
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = what;
msg.obj = new AsyncResult(userObj, result, exception);
h.sendMessage(msg); // 把数据给注册对象的Handler发送Message
}
}
public Handler getHandler()
{
if (refH == null)
return null;
return (Handler) refH.get();
}
// 拥有 3 个成员变量,它们的值都是构造方法中注册对象传递过来的
WeakReference refH; // 存储 Handler 对象的弱引用
int what; // 注册对象用来区分不同的 Registrant 对象,注册对象可能会注册很多 Registrant
Object userObj;
}
RegistrantList 类跟 Registrant 类似,该类中有一个 ArrayList,每注册一次就创建一个 Registrant 对象后加入到 ArrayList中,而internalNotifyRegistrants 方法中遍历调用每个 Registrant 对象的 internalNotifyRegistrant 方法。
接下来看一下 mRingRegistrant 的注册方法,在 BaseCommand 类中。
/* BaseCommand.java */
// 很简单的一个方法,就是用注册对象的三个变量把mRingRegistrant实例化
@Override
public void setOnCallRing(Handler h, int what, Object obj) {
mRingRegistrant = new Registrant (h, what, obj);
}
@Override
public void unSetOnCallRing(Handler h) {
if (mRingRegistrant != null && mRingRegistrant.getHandler() == h) {
mRingRegistrant.clear();
mRingRegistrant = null;
}
}
PhoneBase 类在构造方法中注册了 mRingRegistrant。
/* PhoneBase.java */
protected PhoneBase(String name, PhoneNotifier notifier, Context context, CommandsInterface ci,
boolean unitTestMode, int phoneId) {
...
mCi = ci;
// 注册mRingRegistrant
mCi.setOnCallRing(this, EVENT_CALL_RING, null);
...
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
AsyncResult ar;
...
switch(msg.what) {
// 在handleMessage方法中处理mRingRegistrant发送的消息
case EVENT_CALL_RING:
Rlog.d(LOG_TAG, "Event EVENT_CALL_RING Received state=" + getState());
ar = (AsyncResult)msg.obj;
if (ar.exception == null) {
PhoneConstants.State state = getState();
if ((!mDoesRilSendMultipleCallRing)
&& ((state == PhoneConstants.State.RINGING) ||
(state == PhoneConstants.State.IDLE))) {
mCallRingContinueToken += 1;
sendIncomingCallRingNotification(mCallRingContinueToken);
} else {
notifyIncomingRing();
}
}
break;
...
}
}
ind 服务机制就是客户端注册 Registrant,RILReceiver 接收消息后调用相应的 Registrant.notifyRegistrant 方法,在该方法中把消息发送给客户端的 Handler,最终在客户端的 handleMessge 方法中处理消息。流程图如下所示。
to be continued…
